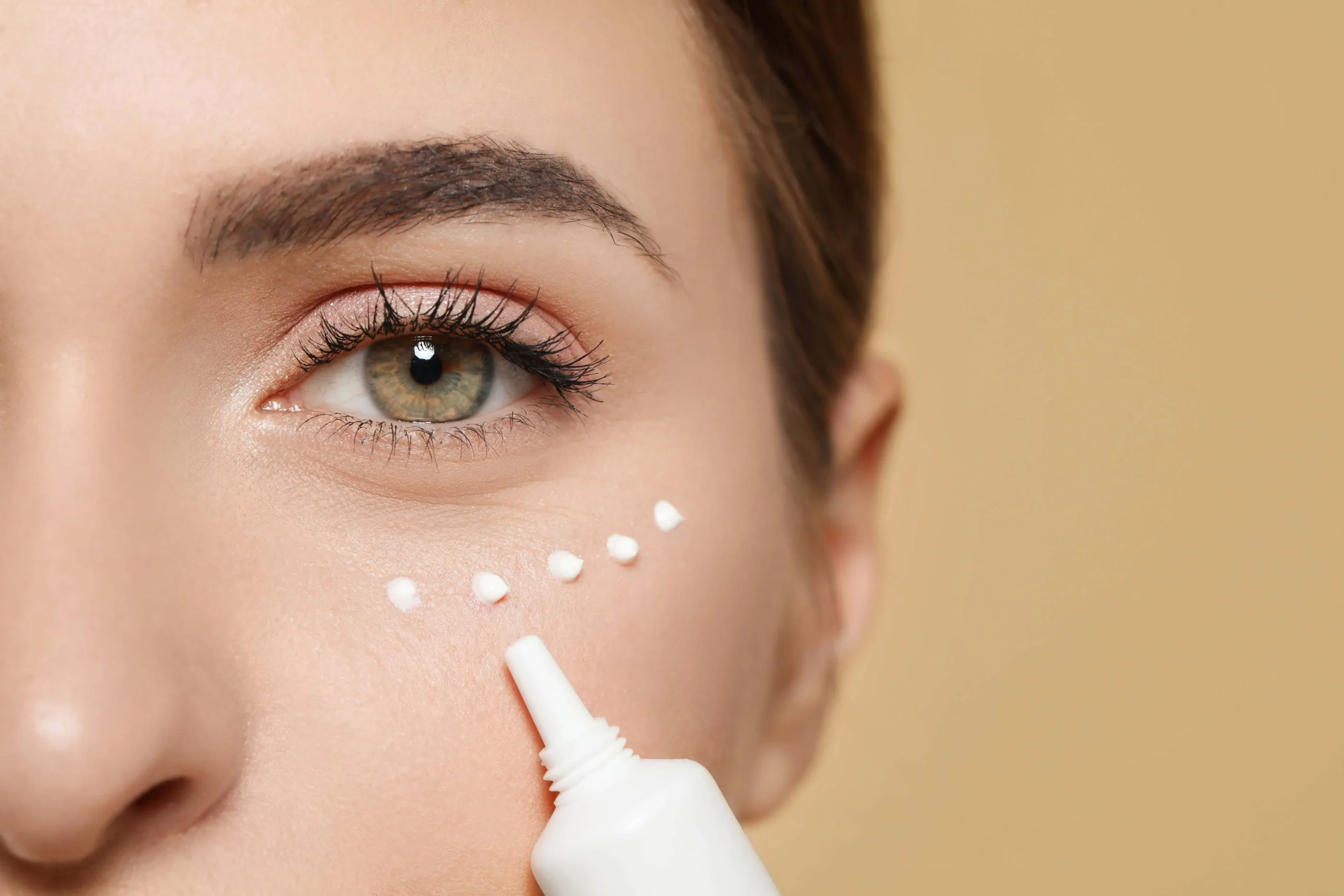
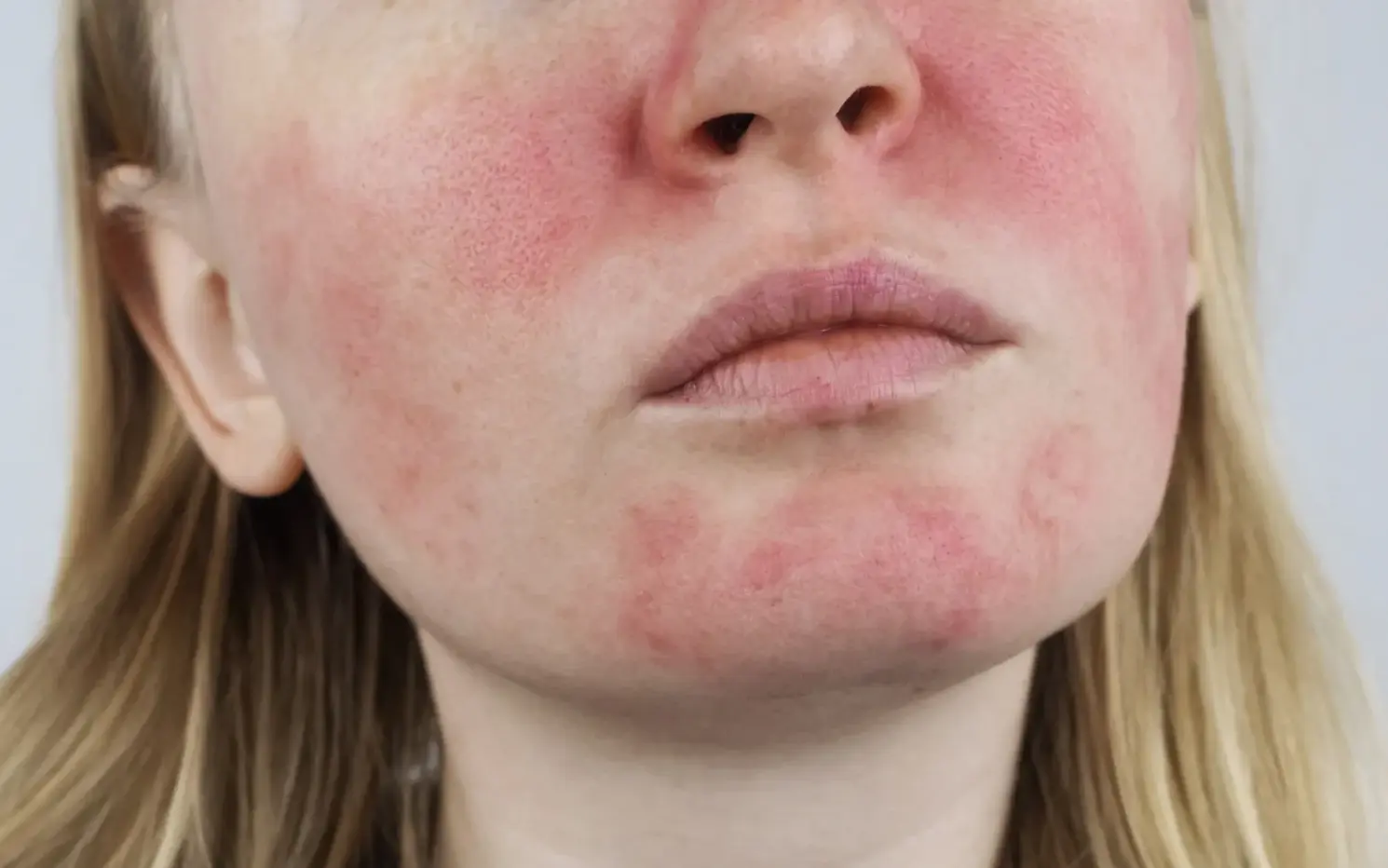
In skincare, more isn’t always more effective. While it might be tempting to believe that higher concentrations of active ingredients in skincare products will yield faster or more dramatic results, using products with dosages above the recommended levels can be both ineffective and potentially harmful. In this blog post, we’ll explore why higher dosages in skincare products are dangerous, the risks involved, and how to use skincare products safely and effectively.
1. Understanding Recommended Dosages
A. What Are Recommended Dosages?
Recommended dosages for skincare products are determined based on extensive research and clinical trials that establish the optimal concentration of active ingredients for safety and efficacy. These dosages are designed to maximize benefits while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. For instance, the recommended concentration of retinol is typically between 0.25% and 1%, while vitamin C serums are usually effective in concentrations ranging from 10% to 20%.
B. Importance of Following Guidelines
Following the recommended dosages ensures that you receive the benefits of the active ingredients without overstressing your skin. Skincare products are formulated with specific ingredient concentrations to work harmoniously with your skin’s natural processes, balancing efficacy with safety.
2. Risks of Excessive Dosages
A. Irritation and Sensitivity
- Overexposure: High concentrations of active ingredients, such as retinoids, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), or vitamin C, can lead to irritation. Symptoms may include redness, peeling, itching, and discomfort. For example, using a retinol product with a concentration higher than recommended can cause excessive dryness and flaking, leading to compromised skin barrier function.
- Sensitization: Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of certain ingredients can cause the skin to become sensitized, making it more prone to reactions from other products or environmental factors.
B. Risk of Allergic Reactions
- Allergic Responses: Excessive dosages can increase the likelihood of allergic reactions, which may present as severe rashes, swelling, or hives. For instance, high doses of vitamin C can trigger an allergic response in some individuals, resulting in significant discomfort and potential damage to the skin.
C. Compromised Skin Barrier
- Barrier Disruption: High concentrations of exfoliants or acids can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier, leading to increased water loss and susceptibility to environmental aggressors. This can result in dryness, increased sensitivity, and a higher risk of infections.
D. Unintended Side Effects
- Systemic Effects: In some cases, applying high concentrations of active ingredients can lead to systemic side effects, particularly if the product is applied over large areas of the body or used frequently. For example, excessive use of products containing hydroquinone, a skin-lightening agent, may lead to systemic absorption and unintended health consequences.
3. Specific Ingredients and Their Risks
A. Retinoids
- Dosage Concerns: Retinoids are effective for reducing wrinkles and improving skin texture, but excessive use can cause severe dryness, irritation, and increased sensitivity to the sun. High concentrations of retinoids can also lead to peeling and redness.
- Recommendations: Stick to concentrations recommended by dermatologists, typically between 0.25% and 1%. Increase the concentration slowly as your skin develops tolerance.
B. Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
- Dosage Concerns: AHAs, such as glycolic acid, are used for exfoliation and improving skin texture. Higher concentrations can cause excessive peeling, irritation, and increased sun sensitivity.
- Recommendations: Use products with AHAs in concentrations ranging from 5% to 10% and limit their application to avoid over-exfoliation.
C. Vitamin C
- Dosage Concerns: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant, but extremely high concentrations can lead to irritation and sensitivity, especially for those with sensitive skin.
- Recommendations: Concentrations of 10% to 20% are effective for most people. Higher concentrations are not necessarily more beneficial and may increase the risk of irritation.
D. Niacinamide
- Dosage Concerns: Niacinamide is known for its anti-inflammatory and barrier-repairing properties. Extremely high doses can lead to skin flushing and redness.
- Recommendations: A concentration of 4% to 10% is typically effective for most people.
4. How to Use Skincare Products Safely
A. Start Slowly
- Patch Testing: Always perform a patch test before using a new product to ensure you don’t have an adverse reaction.
- Gradual Introduction: Introduce new products into your routine gradually, starting with lower concentrations and increasing as your skin adjusts.
B. Follow Instructions
- Adherence to Directions: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application and dosage. Using more than the recommended amount does not accelerate results and may increase the risk of adverse effects.
C. Consult a Dermatologist
- Professional Advice: For personalized advice on product concentrations and combinations, consult a dermatologist. They can recommend products and concentrations suited to your skin type and concerns.
D. Monitor Your Skin’s Response
- Observe Changes: Monitor how your skin responds to new products. If you encounter persistent irritation or discomfort, stop using the product and consult a professional.
Conclusion
Using skincare products with dosages higher than recommended can be detrimental to your skin’s health. While it might seem like a good idea to use higher concentrations for quicker results, the risks of irritation, sensitivity, and other adverse effects outweigh the potential benefits. To achieve the best results, adhere to recommended dosages, start with lower concentrations, and consult with skincare professionals to tailor your routine to your individual needs. Remember, effective skincare is about balance and consistency, not excess.