Retinol has been around for centuries and has shown to have a variety of benefits. In the 1920s, scientists isolated and named the compound used for preventing night blindness “retinol” due to its association with the retina of the eye. During the 1960s and 1970s, researchers began investigating retinol’s effects on skin health and aging. It was found to stimulate collagen production, promote cell turnover, and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. This led to the development of retinol-based skincare products, such as creams and serums. Today there are a variety of forms of retinoids and different classifications, potencies and forms out on the market.
What is the difference between Retinols and Retinoids?
Retinol is a form of Vitamin A used in a variety of topical anti aging creams and is highly effective for stimulating collagen and reducing the appearance of wrinkles while improving texture and promoting a youthful complexion. It is typically found in over-the-counter skin care products. It is considered a milder and less potent version of retinoids. Retinol is not active when applied to the skin but is converted into retinoic acid, the active form of vitamin A, by enzymes in the body.
Retinoids are a broader class of compounds that include both naturally occurring and synthetic derivatives of vitamin A. They are available in different forms, including tretinoin (retinoic acid), adapalene, and tazarotene, which are commonly used in prescription-strength topical treatments. Retinoids are more potent than retinol and have a direct effect on the skin without requiring conversion. They interact with specific receptors in the skin cells, promoting cell turnover, reducing inflammation, and stimulating collagen production. Retinoids are highly effective for treating various skin conditions such as acne, photoaging (sun damage), and hyperpigmentation. However, they can also cause more side effects, including dryness, peeling, redness, and sensitivity to sunlight
What are the benefits of Retinoids?
-
Reduction of Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Retinol is renowned for its ability to diminish the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. It works by stimulating collagen production, the protein responsible for maintaining skin’s elasticity and firmness. As a result, the skin becomes smoother, plumper, and more youthful.
-
Improvement in Skin Texture: Uneven skin texture, characterized by roughness, dullness, or uneven tone, can be beautifully transformed with retinol. By accelerating cell turnover, retinol helps shed dead skin cells, revealing fresh, glowing skin underneath. This leads to a refined and smoother complexion.
-
Minimization of Hyperpigmentation: Sunspots, age spots, and other forms of hyperpigmentation can be frustrating signs of aging. Luckily, retinol comes to the rescue! It regulates melanin production, the pigment responsible for skin coloration, helping to fade existing dark spots and prevent new ones from forming.
-
Enhanced Skin Hydration: Aging skin tends to lose moisture, resulting in dryness and a lackluster appearance. Retinol promotes enhanced hydration by strengthening the skin’s moisture barrier, allowing it to retain moisture more effectively. This helps to restore a youthful, plump, and dewy complexion.
-
Reduction of Acne and Breakouts: It’s not just the aging process that retinol combats; it’s also a powerful weapon against acne and breakouts. By unclogging pores and regulating sebum production, retinol helps to prevent and heal blemishes, giving you a smoother, clearer complexion.
How to integrate Retionols into one’s skincare routine?
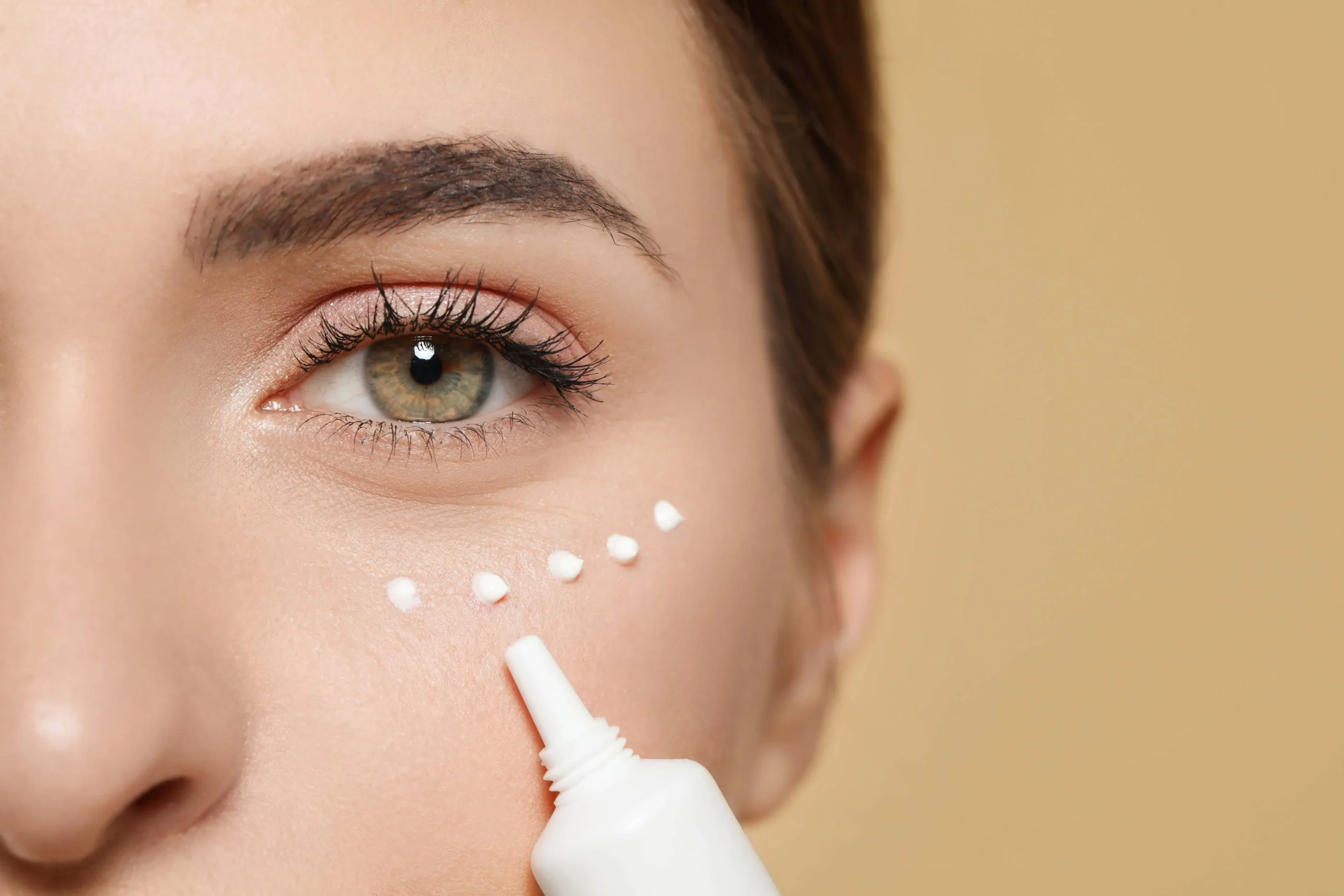
Retinol is a potent ingredient that requires proper usage and care. Start with a low concentration and gradually increase as your skin adapts. Talk to your provider of the best retinol choice for your skin. We recommend the medical grade, Soyier Skin Crème de Retinol Medical Retinol Cream 0.5%! Apply at night time before moisturizing and after serums. Always use sunscreen during the day when incorporating retinol into your routine, as it can increase sun sensitivity.