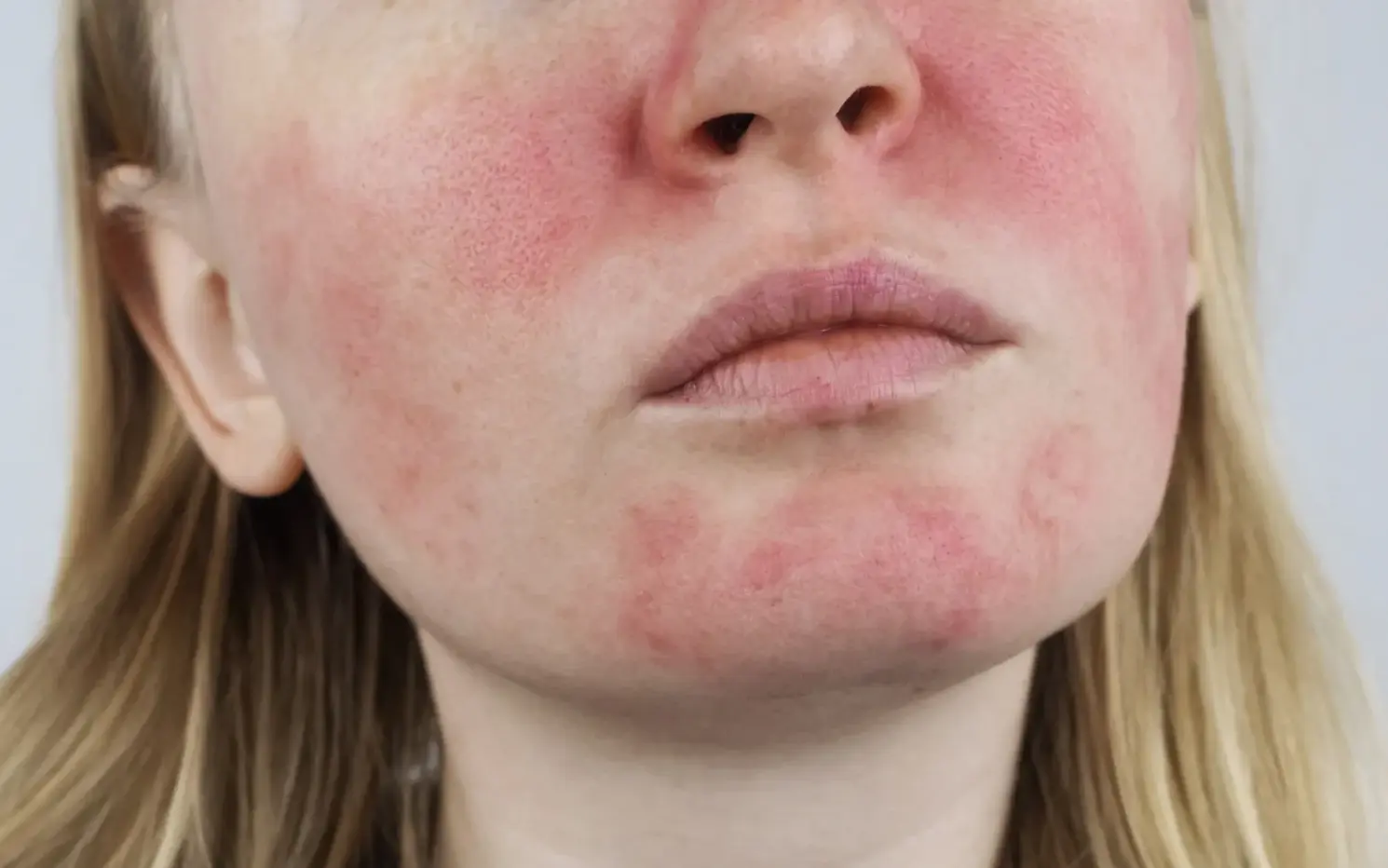
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, irregularly shaped patches on the skin, typically found on the face. While it’s not harmful, melasma can be challenging to manage and can affect a person’s confidence. In this blog post, we’ll explore what melasma is, its causes, and the most effective treatments available to help you manage and improve this condition.
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that causes dark, frequently symmetrical patches on the skin. Other names for it include “chloasma” and “the mask of pregnancy.” These patches most commonly appear on the face, including the cheeks, forehead, nose, and chin, but can also occur on the sun-exposed areas. Melasma is more prevalent in women, particularly those with darker skin types, and can be exacerbated by hormonal changes and sun exposure.
Causes of Melasma
The development of melasma can be attributed to multiple factors:
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy,the use of oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy, are strongly linked to melasma. Because of this, it is often called the “mask of pregnancy.”
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation from the sun can cause melasma or worsen it. UV light stimulates melanocytes (the cells that produce pigment), leading to increased melanin production and hyperpigmentation.
- Genetics: If your family members have melasma, you may be more likely to develop it yourself.
- Skin Irritation: Certain skincare products or procedures that irritate the skin can exacerbate melasma, especially if they cause inflammation or a disruption in the skin barrier.
- Medication: Some medications, particularly those with hormonal components, can contribute to the development of melasma.
How to Treat Melasma
While melasma can be persistent and challenging to treat, several strategies can help manage and reduce its appearance. Here are some effective treatment options:
1. Sun Protection
Sun protection is crucial in managing melasma. Daily use of a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF30 or higher can prevent further darkening of the patches and help in the fading process.
Look for sunscreens that offer protection against both UVA and UVB rays and consider using physical blockers like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
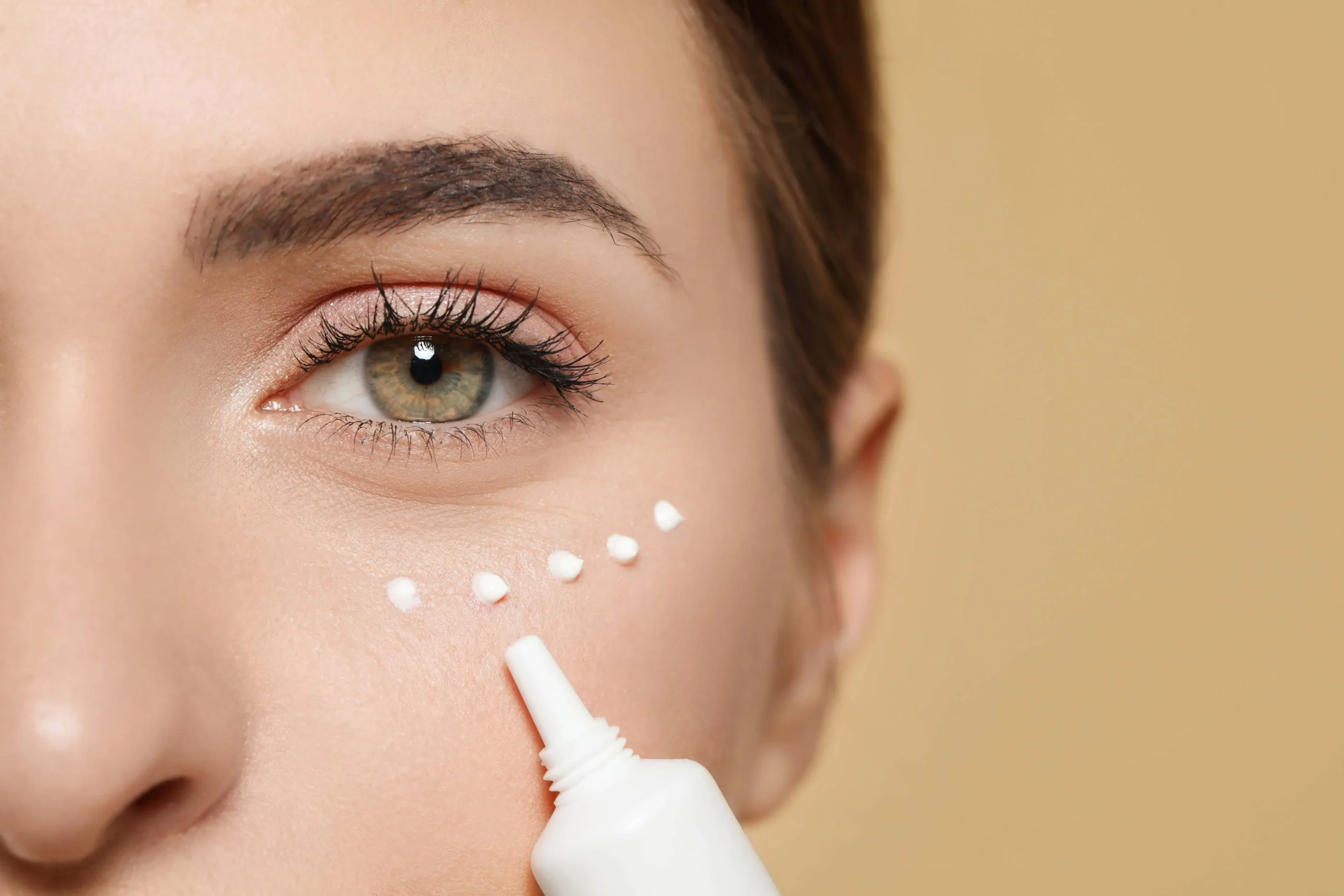
2. Topical Treatments
Several topical treatment scan help lighten melasma:
- Hydroquinone: This is a common skin-lightening agent that works by inhibiting melanin production. It is often used in combination with other ingredients for enhanced
- Tretinoin: Also known as retinoic acid, tretinoin helps increase cell turnover and can improve the appearance of melasma by promoting the shedding of pigmented skin cells.
- Azelaic Acid: Azelaic acid has both anti-inflammatory and skin-lightening properties, making it effective for treating melasma.
- Vitamin C: This antioxidant helps to brighten the skin and inhibit melanin production, which can aid in reducing melasma.
- Kojic Acid: Another skin-lightening agent that can help reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation.
3. Chemical Peels
Professional chemical peels use acids like glycolic acid or salicylic acid to exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation. These peels can help improve skin texture and tone, but they should be performed by a qualified dermatologist to minimize the risk of irritation or worsening of melasma.
4. Laser Treatments
Laser therapies, such as fractional laser or intense pulsed light (IPL), can target the melanin in the skin and help reduce hyperpigmentation. Laser treatments should be done under the guidance of a dermatologist experienced in treating melasma to ensure safety and effectiveness.
5. Avoid Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers that worsen melasma is crucial. For some individuals, hormonal changes or certain medications can exacerbate the condition. If you suspect that a particular medication or hormonal treatment is contributing to your melasma, consult your healthcare provider for alternatives.
Prevention Tips
While melasma can be challenging to prevent entirely, you can take steps to reduce your risk:
- Consistent Sun Protection: Make sunscreen a daily part of your routine, even on cloudy days or when indoors. If you spend a lot of time in the sun, reapply every two hours.
- Avoid Excessive Sun Exposure: Spend as little time as possible in the sun, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Use Gentle Skincare Products: Avoid using products that can irritate your skin or trigger inflammation. Select products that are gentle and non-comedogenic based on your skin type.
- Regular Dermatological Checkups: Regular visits to a dermatologist can help monitor your condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
Conclusion
Melasma is a common but manageable skin condition that requires a combination of sun protection, topical treatments, and professional care. By understanding its causes and implementing the right strategies, you can effectively manage melasma and improve your skin’s appearance. If you struggle with persistent melasma, consulting a dermatologist can provide personalized treatment options tailored to your needs.
Keep in mind that managing melasma requires persistence and patience. With the right approach, you can achieve clearer, more even-toned skin and regain your confidence.